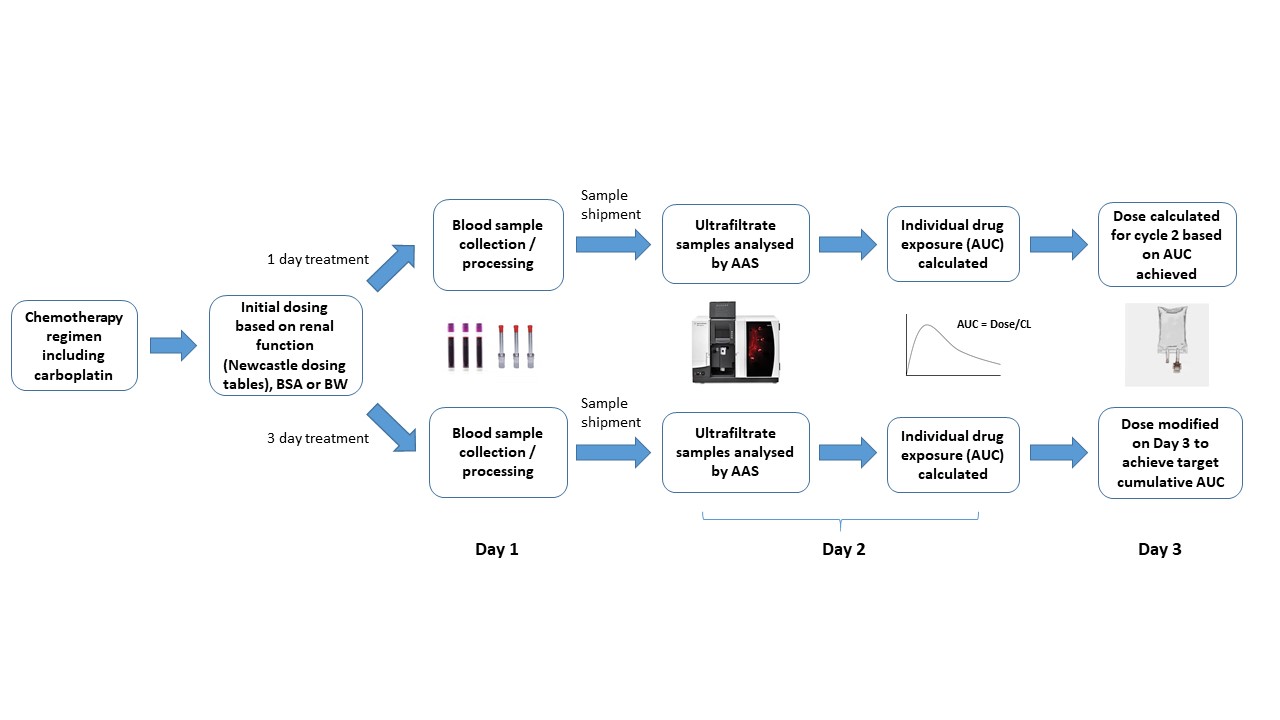
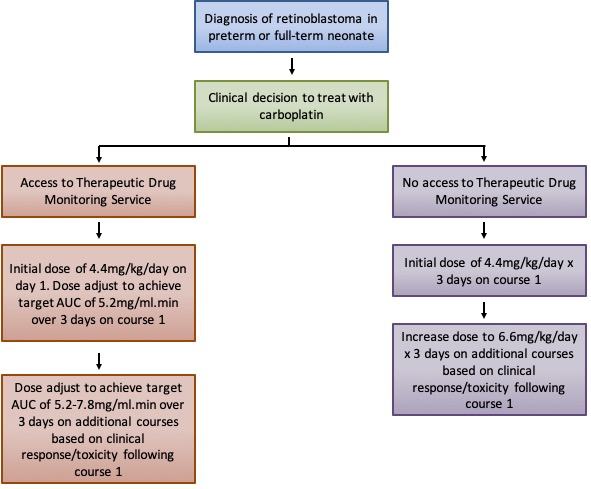
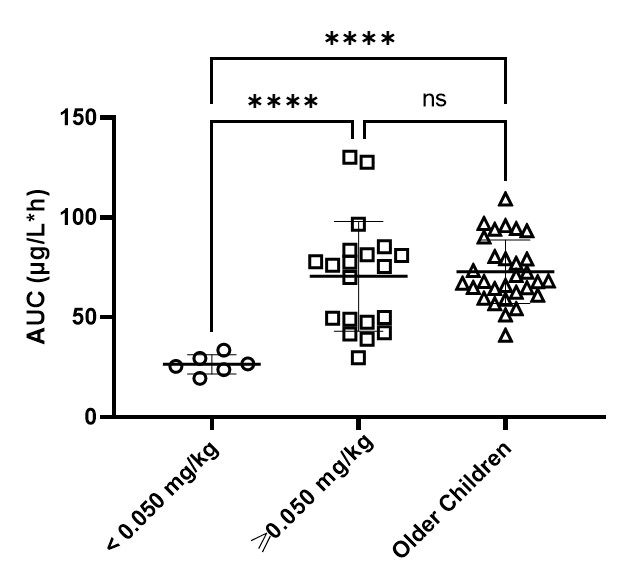
A
Grade
Cyclophosphamide
PK studies in children (including infants) have been published. A higher CL had been found in younger children, resulting in a higher exposure to metabolites.
Level 1
Population PK model including infants
| Author | Method | Number of Patients/Infants(<1yrs) | Age(yr), Median(range) | Age related findings | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yule (1996) | One compartment popPK model | 38 / 5 | 4 (0.2-18) | No additional effect of age on PK parameters that was not explained by BSA. | ||
| Campagne (2020) | Two compartment popPK model (cyclophosphamide). One compartment popPK model (metabolites). Age, phenobarbital treatment and CYP2B6 polymorphism correlated with PK. | 171 / 42 | 1.8 (0.07-4.9) | Infants had higher exposures of the active metabolite compared to older children. Suggested to decrease dose by 20% in young infants to achieve similar exposures to older children. | ||
| Barnett (2021) | Two compartment popPK model. Allometric scaling for BSA. CYP2B6 polymorphism and eGFR were included as covariates for CL. | 25-Dec | 1 (0.33-2) | No effect of age on PK within this study. However, CL (mL/min/m2) of cyclophosphamide and AUC of metabolites in children <2 years old significantly higher than those reported in older children. |
Level 2
PK model including infants or PopPK model without infants
| Author | Method | Number of Patients/Infants(<1yrs) | Age(yr), Median(range) | Age related findings | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yule (1997) | PopPK model (compartments not described) | 14-Jan | 8.5 (0.7-17) | Effect of age on PK was not studied. | ||
| Yule (2001) | One compartment popPK model | 13 / 0 | 4 (2-17) | No effect of age on PK parameters. | ||
| Yule (2004) | One compartment popPK model | 36 / 0 | 8 (2-16) | Effect of age on PK was not studied. | ||
| McCune (2009) | Multicompartment popPK model (one compartment for cyclophosphamide, three compartments for metabolites) | 22 / 0 | 3.16 (1.3-9.37) | Cyclophosphamide AUC associated with patient age and BSA. | ||
| Balasubramanian (2012) | Two compartment popPK model (cyclophosphamide), One compartment popPK model (metabolites), BW, age and CYP2C19 polymorphism were included as covariates for CL | 55 / 0 | 7.3 (2-14) | Decrease in CL (L/h/kg) with patient age. | ||
| Navid (2013) | Two compartment popPK model | 19 / 0 | 9.2 (1.2-24.5) | Effect of age was not studied. | ||
| Veal (2016) | Two compartment popPK model, Allometric scaling for BSA. CYP2B6 polymorphism and eGFR correlated with CL. | 49 / 0 | 11.7 (3.5-18.7) | No effect of age on CL (L/h/m2). |
Level 3
Non-compartmental PK study or PK model without infants
| Author | Method | Number of Patients/Infants(<1yrs) | Age(yr), Median(range) | Age related findings | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Juma (1984) | Non-compartmental pharmacokinetics, Kenyan patients | 8 / 0 | NS (1-4) | Effect of age not studied in this patient group. However, CL (mL/h/kg) values here are higher than those reported in adults. | ||
| Tasso (1992) | Non-compartmental pharmacokinetics | 09-Feb | 4.3 (0.7-16.8) | Effect of age not studied in this patient group. However, CL (L/h/m2) values here are higher than those reported in adults. |
Level 5
Mechanism-based reasoning or expert opinion
| Author | Method | Number of Patients/Infants(<1yrs) | Age(yr), Median(range) | Age related findings | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Balis (2017) | Mechanism-based development of dose bands based on BSA intervals |